Exercise Stress Testing
Exercise stress testing is a useful outpatient test performed by a cardiologist.
The principle is exercise the heart to a certain level (85% of the calculated maximum HR which is 220-age) and assess for signs of impaired coronary blood flow to the heart muscle. These signs may be:
1. Chest pain
2. Severe dyspnea
3. Certain abnormal heart rhythms
4. Changes in the ECG
5. Abnormal motion of the heart wall on ultrasound.
What is it? Measures the performance and capacity of the heart. In many cases, the test is carried out to assist in making a diagnosis of coronary artery disease. Other uses of the test include evaluating a patient’s capacity to undertake certain physical activities or occupations, assessment of prognosis in patients with heart disease and the effect of treatment on symptoms.
Preparation: Patients will need loose comfortable clothing and comfortable walking shoes. It is preferable that no food is taken two hours before the test and any meals consumed on the day are light.
How long will it take? You should allow about 45 minutes for the appointment.
What happens during the test? You will be asked to walk on a treadmill and the speed and gradient of the treadmill increasing every three minutes. The test is stopped if you develop symptoms such as fatigue, breathlessness, tired legs, chest pain or other symptoms or when you reach an appropriate target. Throughout the test your pulse, blood pressure and electrocardiogram will be monitored. If there is any abnormal change in any of these observations, the test will be stopped.
What happens after your test? If you are having a stress ultrasound (or echocardiogram), ultrasound pictures will be taken of your heart both before and immediately after the stress test If at any time during the test you are feeling unwell in any way, report the symptom immediately.
Please note
1. A stress ECG can be normal in the presence of a significant coronary blockage up to 30% of the time in males and 40% of the time in middle aged females - i.e. a false negative
2. A stress echocardiogram (ultrasound) is far more accurate and will be normal in 10 to 15% of patients in the presence of a coronary blockage.
Therefore, chest pain without an alternate cause and a normal exercise stress test should usually be followed by imaging of the coronary arteries with either a CT scan or formal coronary angiogram.
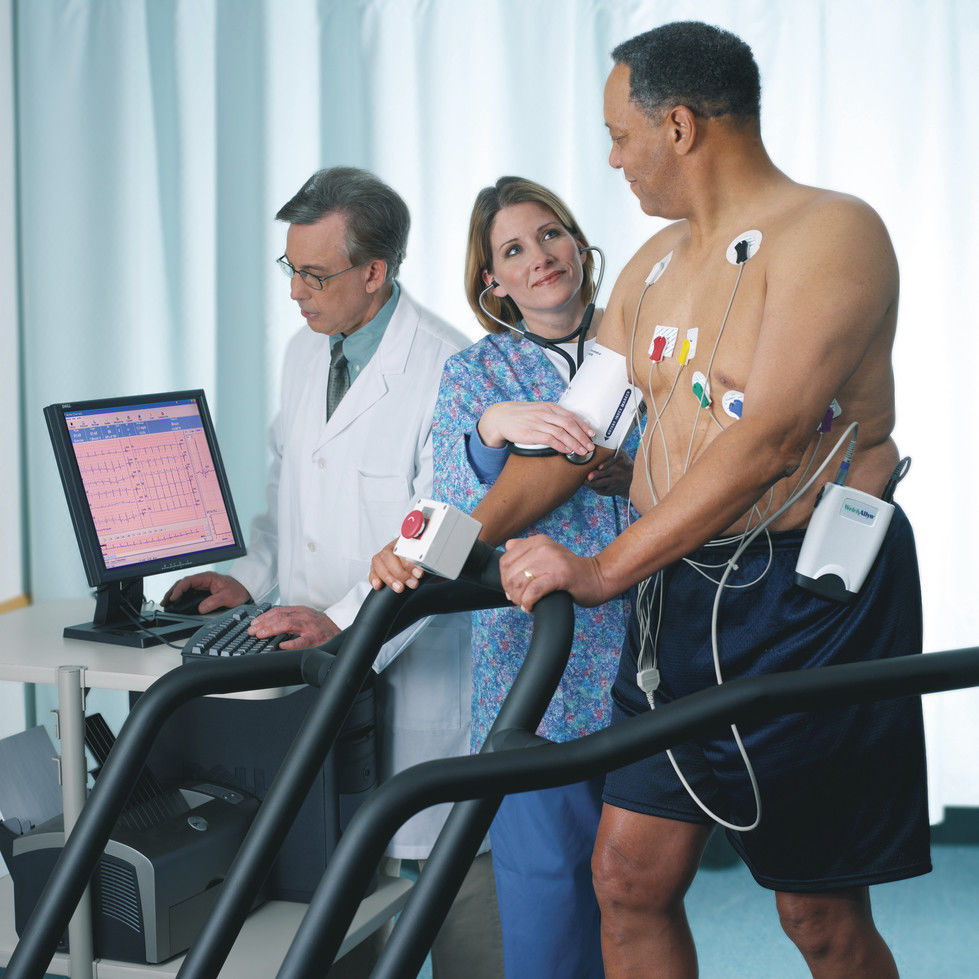
A stress test is used in cardiology for different reasons
To exclude significant blockages in the coronary arteries if a patient presents with cardiac symptoms (i.e. chest pain or shortness of breath)
- If a patient has had previous bypass surgery or stents - to ensure that these are open and providing the heart with sufficient blood flow
- In asymptomatic patients routinely if they perform certain occupations e.g. train drivers, bus drivers, commercial pilots
The principle is that the heart is stressed and the heart muscle is assessed either directly or indirectly
Forms of stress to the heart include
- Exercise
- Medication
- Combination of both
The heart function is checked by
- ECG (Exercise ECG)
- Heart ultrasound (Exercise Echo)
- Blood flow scanning (MIBI scan)
Each method has advantages and disadvantages. Its important to realise that NO stress test is perfect. Stress testing can miss a blockage 10 to 30 % of the time depending on the test used. Therefore, If you continue to have symptoms despite a negative stress test, a coronary angiogram is usually required.
If a stress test is positive, this does not necessarily mean a coronary blockage exists. These investigations can be falsely positive. However a coronary angiogram is usually needed to clarify the situation.
Stress Testing without exercise
If you are unable to exercise, the options include a nuclear medicine perfusion scan performed in a radiology facility, CT coronary angiography, or an invasive coronary angiogram.
The choice is an individual one based on many factors and is best decided by an experienced cardiologst.